Determining the Value of the Ideal Gas Constant
Teacher Notes
- This procedure is written up supposing you have a balance that will read to at least mg.
If you have only a cg balance, then find the mass of a longer piece of Mg (approximately 1
m) and calculate the mass of the shorter pieces by ratio from this value. This gives
acceptable results, provided the Mg ribbon is reasonably consistent.
- Calculate the approximate mass required by measuring the barometric pressure before the
experiment. Each piece must be selected so that it will not produce more than 50 mL of
gas. You can calculate the maximum length using this formula: Maximum mass = 4.4 x 10-4
P where P is in kPa (this formula calculates the mass required to produce 45 mL of gas,
allowing a slight safety margin). Multiply by 3 to get the length required to do three
trials.
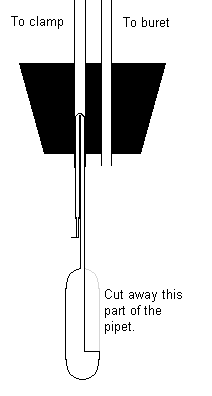
- Make the plastic scoop by cutting a 5 mL Berol plastic pipet lengthwise, leaving a small
bowl at the end. Then fold over the stem and insert it into the glass tubing connected to
the clamp. The pipet will stay in place from friction. The bowl needs to be deep enough
that the Mg won’t fall out too easily, but not so deep that you can’t shake it
out into the acid when you want to.
Copyright © 1998 - 2008 David Dice

