 |
Ba2+ ions are added and a lot of precipitate of BaCrO4 forms. |  |
The NO3- part of the barium nitrate has no effect in this reaction -- it is just a spectator ion. However, the Ba2+ can react with the CrO42- to form a solid precipitate of BaCrO4. The solubility of BaCr2O7 is much higher, and it does not form a precipitate.
The primary role of the Ba2+ ions in this reaction is to show the amount of CrO42- present. The more CrO42- there is, the greater the quantity of precipitate that will be formed.
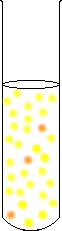
When Ba2+ ions are added to
a chromate solution, a lot of BaCrO4
precipitate forms.
 |
Ba2+ ions are added and a lot of precipitate of BaCrO4 forms. |  |
When Ba2+ ions are added to
a dichromate solution, a small amount of BaCrO4 precipitate forms.
 |
Ba2+ ions are added and a small
amount of precipitate of BaCrO4
forms. Most of the Ba2+ ions remain unreacted. |
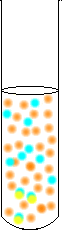 |
What would happen if you added acid to the dichromate solution?
Because the reaction of the H+ ions will cause the small amount
of CrO42- ions present to become even smaller, the small amount of precipitate will
dissolve. There are no longer enough CrO42-
ions for the Ba2+ to react with.
 |
When H+ is added the equilibrium shifts to produce even more Cr2O72- |  |
So, when Ba2+ is added there is
not enough CrO42- for a
precipitate to form. The Ba2+ remains unreacted. |
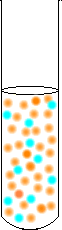 |
What would happen if you added sodium hydroxide to the dichromate solution?
Because the reaction of the OH- ions will remove some of the H+, this will cause a large amount of CrO42- ions to form in the
solution. Much more precipitate will form since there are now enough CrO42- ions for the Ba2+ to react with.
 |
When OH- is added the equilibrium shifts to produce even more CrO42- | 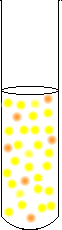 |
So, when Ba2+ is added there is now enough CrO42- for a precipitate to form. |  |
Copyright © 1998 - 2008 David Dice