| For simplicity, the symbol H+ is being used for the acid proton, rather than the Brönsted-Lowry hydronium ion H3O+. All ions in these equations are aqueous, but the (aq) symbol has been omitted for brevity. |
One of the simplest ways to think about the effect of adding sodium
hydroxide is to realize that it removes H+ ions because of this reaction: H+
(aq) + OH-(aq) ![]() H2O (l)
H2O (l)
So sodium hydroxide removes H+ ions. If there was no
chemical reaction then adding NaOH should decrease the amount of H+(aq).
The original H+in the water would decrease to become H+ Since the H+ is colorless, we
wouldn't see any color change. But there is going to be a chemical
reaction. From le Châtelier's principle, we know the reaction will try to restore
some of the H+ we have removed. The required H+ comes
from turning some of the Cr2O72- back into the CrO42-.
For the chromate solution (remember that the original solution is an equilibrium, so it
contains mostly yellow chromate, but a bit of orange dichromate):
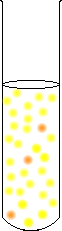 |
add some OH- (aq) and it becomes |
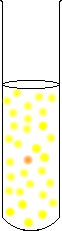 |
a slightly more yellow solution, and probably not noticeable | ||||||
Notice, that the H+ is greater than it would be if there was no reaction, but less than it was at the beginning. Because there already was a lot of yellow dichromate, the change is not very noticeable. |
|||||||||
For the dichromate solution (remember that the original solution is also an equilibrium, so it contains mostly orange dichromate, but a bit of yellow chromate):
 |
add some OH- (aq) and it becomes |
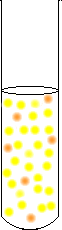 |
a much more yellow solution | ||||||
Notice, that the H+ is greater than it would be if there was no reaction, but less than it was at the beginning. Because there is now a lot more yellow chromate, and a lot less orange dichromate, the change in color is very noticeable. |
|||||||||