Partial Pressure: in
a mixture of gases, each gas behaves independently of the others (assuming the gases
behave ideally). The total pressure is then the sum
of the pressures each gas would exert, if it were in the container by itself. This
law was first discovered by John Dalton, so is called Dalton's law of partial
pressures. It can be expressed mathemtaically as: PT = Pa + Pb
+ Pc + ...
| where: |
|
|
| PT |
= |
the total pressure of the gas |
| Pa |
= |
the part of the pressure due to gas A |
| Pb |
= |
the part of the pressure due to gas B |
| Pc and so on |
= |
the part of the pressure due to gas C, and so on for as many gases as are
mixed together |
PET bottles: PET, short for polyethylene
terephthalate, a commonly recycled household plastic material, represents
approximately 30 percent of the plastic bottle market and is used to package a wide
variety of food and beverage products such as soft drinks, juices, edible oils, liquor and
peanut butter. PET is valued for its clarity, toughness, and inpenetrability by
carbon dioxide. Many products are made from recycled PET including carpets,
insulating material in garments and sleeping bags (fiberfill), and other bottles and
containers, scouring pads, and auto parts.
|
 |
|
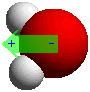 Oxygen atoms have a greater attraction for electrons than
do hydrogen atoms. Because of the shape of a water molecule, this results in a polar
molecule that has the positive charge oriented between the two hydrogens, with the
negative charge oriented towards the oxygen. |
Polarity effects: in a solution, the
positive and negative charges on ions will tend to make the ions clump together, and cause
the solvent molecules to line up in certain orientations. Some solvent molecules,
such as water are already substantially polar, and so will align themselves readily with
ions. Other solvents are quite "polarizable" – their electrons can be
displaced by the charge on an ion, and so will themselves become slightly polar, even
though in the pure solvent they are not. Such polarity effects allow substances to
form intermolecular attractions, and therefore solutions.
Polymer: long chain molecules, generally with
a hydrocarbon skeleton, and other functional groups attached to give the materials
specific characteristics. Polyethylene is a polymer of ethylene linked end to end,
with as many as 200,000+ atoms in the molecule. Polymers are commonly called
plastics.
Potential energy: energy an object
posseses because of its position. Chemical bond energy is potential energy because
it depends on the position of one atom with respect to another in a molecule.
Pressure: force per unit area. The SI
unit of pressure is Pascals (Pa); however, in most pressure measurements this will be
expressed as kPa. The atmospheric pressure
at the Earth's surface is about 101.3 kPa.
